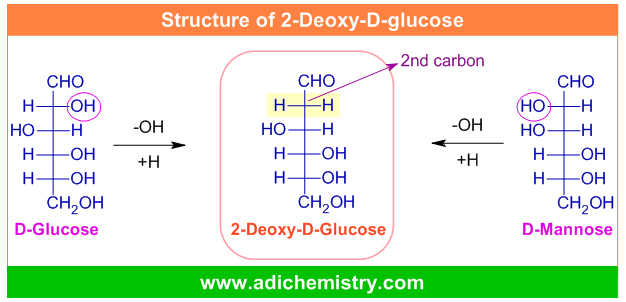
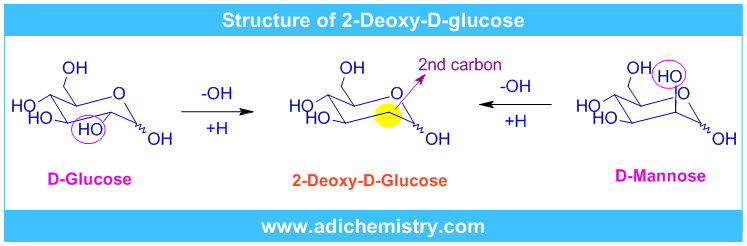
2-Deoxy-D-glucose, abbreviated as 2-DG, with the formula C6H12O5 is a derivative of D-glucose molecule (C6H12O6). It is obtained by replacing the 2-hydroxyl group in glucose molecule (or in mannose molecule, a C-2 epimer of glucose) by hydrogen.

During the first step of glycolysis in living cells, the 2-deoxy-D-glucose competes with D-glucose and therefore it is preferentially converted into 2-deoxy-D-glucose-6-phosphate in presence of enzyme hexokinase.
The 2-deoxy-D-glucose-6-phosphate cannot be catalyzed further by phosphoglucoisomerase (2nd step of glycolysis). This will result in the accumulation of 2-deoxy-D-glucose-6-phosphate in the cell and inhibits overall glycolysis process and thus by hampering the growth of cells. (You may ask the question what will happen to healthy cells.)
Therefore, it is suggested that 2-DG can effectively and selectively inhibits the growth of cancer cell as well as the cells infected by COVID-19. Thus it is recommended as an effective anti-tumor agent and anti-COVID-19 drug.
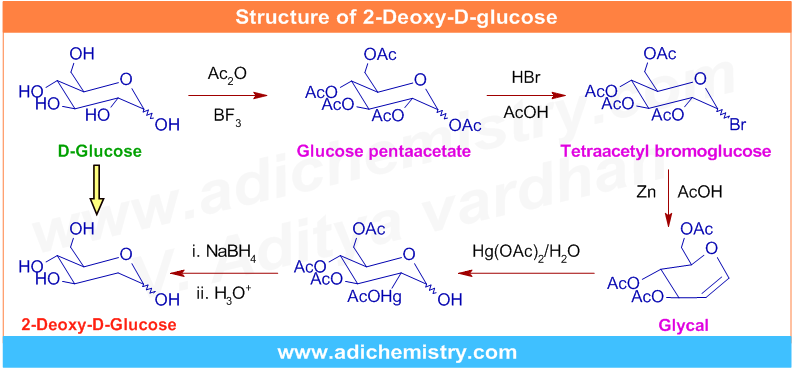
Since it is the analogue of D-glucose, we can propose a synthetic strategy for the preparation of 2-Deoxy-D-glucose (2-DG) from naturally occuring D-glucose as shown below. However, remember that it may or may not be the best method to synthesize 2-DG. Following scheme is proposed to initiate a healthy discussion in organic synthesis.