Answer:
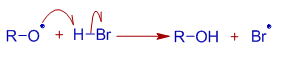
The anti markonikov's addition of HBr to unsymmetrical alkenes in presence of peroxides and light is a free radical addition reaction. The crucial step is abstraction of H* free radical from the hydrogen bromide by the organic free radical (alkoxy or alkyl free radicals).

This step is exothermic (why?) and hence formation of Br* free radical is feasible. Hence the reaction can proceed further.
However, HCl and HI do not undergo any free radical additions to alkenes in presence of peroxides.
Reasons:
In case of HCl, the abstraction of H* from HCl is endothermic (why?) and hence further reaction is not possible.
And in case of HI , even though the abstraction of H* from HI is exothermic, the addition of I* free radical to alkene is endothermic. Hence addition with HI is less likely to occur.
Why the abstraction of H* free radical from HBr is exothermic, whereas it is endothermic with HCl?
Since H-Cl bond is stronger than H-Br, breaking H-Cl bond requires more energy. The energy released in the formation new O-H bond cannot compensate for this as with HBr. Hence the abstraction from H-Cl is endothermic.
What about HF?
H-F bond is even more stronger than H-X bonds in other halides. Hence we can safely assume that in this case too the abstraction of H* free radical is not feasible due to endothermic nature.
Remember that addition of H-Br through electrophilic addition mechanism is also not possible under normal conditions due to same reason.
1) What are endothermic and exothermic reactions?
2) What is anti-markonikov's rule?
3) What is Kharash effect?
4) What is the mechanism of electrophilic addition reaction of alkenes?
Author: Aditya vardhan Vutturi