Compound-1
The systematic IUPAC name of the following organiccompound is arrived at by following the steps described below.
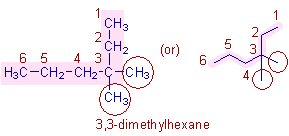
* The parent chain contains 6 carbons and therefore the root word is "hex".
Note: The parent chain need not be straight.
* The bonds between all the carbons are single bonds i.e., saturated. Hence the primary suffix is "ane".
Note: In IUPAC nomenclature, only look at the bonds between carbon atoms to decide whether it is saturated or unsaturated.
* There is no functional group. Hence no need of secondary suffix.
* There are two methyl groups on 3rd carbon (shown in circles). Hence the prefix is 3,3-dimethyl. The numbering is done such that the methyl groups get the least number.
Note: The prefix "di" is used to indicate the presence of two methyl groups.
* Hence the complete name is: 3,3-dimethyl + hex + ane = 3,3-dimethylhexane.
Compound-2
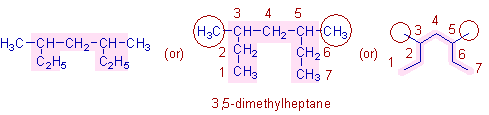
* The longest chain contains 7 carbons. Hence the root word is "hept".
Note: Do not come under the impression that there are two ethyl groups on the straight chain containing only 5 carbons. Actually the carbons in C2H5 are part of the parent chain. See the expanded chain also for the clarification.
* The primary suffix is "ane" since there is no unsaturation.
* There is no functional group. Hence there is no secondary suffix.
* There are methyl groups on 3rd and 5th carbons (shown in circles). Hence the prefix is 3,5-dimethyl.
* Hence the complete name of this organic compound is: 3,5-dimethyl + hept + ane = 3,5-dimethylheptane.
Compound-3
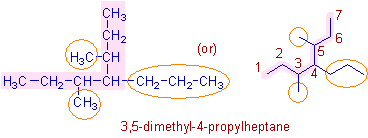
* The parent chain is so chosen that it contains most substituents. It has 7 carbons and hence the root word is "hept".
Note: There are three chains with 7 carbons. However the chain with more number of substituents (3) is taken as parent chain (see below).

* The primary suffix is "ane".
* No functional group. Hence no need of using secondary suffix.
* There are methyl groups on 3rd and 5th carbons as well as one propyl group on 4th carbon atom on the parent chain. Hence the prefix is 3,5-dimethyl-4-propyl.
Note: The dimethyl is written first since it is alphabetized under 'm' and not 'd'.
* The complete IUPAC name is: 3,5-dimethyl-4-propyl + hept + ane = 3,5-dimethyl-4-propylheptane.
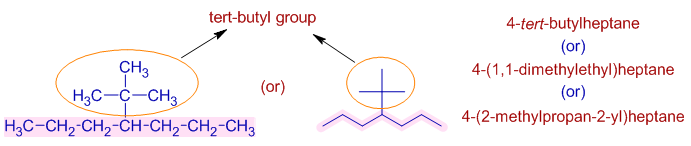
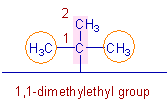
* There is tert-butyl group on 4th carbon.
* The tert-butyl group can also be named as "1,1-dimethylethyl".
The parent chain of this group is so chosen that the first carbon is attached to the main chain.
In this case, the parent chain of the group contains 2 carbons. Also there are two methyl groups on the 1st carbon. Hence the name of this group is "1,1-dimethylethyl".
Since this group is present on the 4th carbon of the main chain, it is mentioned as 4-(1,1-dimethylethyl) in the name.
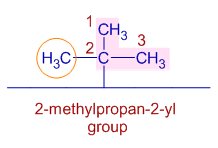
* However, according to a new system of IUPAC nomenclature the tert-butyl group can also be named as "2-methylpropan-2-yl".
According this new system, the longest chain is so chosen that one of the carbon is attached to the main chain. This need not be the first carbon. The numbering starts from that side to give lowest numbers to the side chains if any. The point of attachment to the main chain is also mentioned within the group name.
In this case, the longest chain of the group contains three carbons. This group is attached to the main chain at its second carbon. Also there is a methyl group on the 2nd carbon. Hence the name is "2-methylpropan-2-yl".
Note: Some students name this organic compound as 2,2-dimethyl-3-propylhexane. They argue that the chain with 6 carbons is to be taken as the parent chain since it contains more number of groups.
But this argument is wrong since there is a longest chain with 7 carbons.
First we have to look at the longest chain.
If we get two or more chains with same number of carbons, then only one should compare the number of substituents.
Compound-5
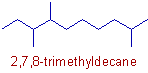
* The parent chain contains 10 carbons. Hence the root word is "dec".
* Primary suffix = "ane"
* No functional group. No need of secondary suffix.
* There are three methyl groups indicated by "2,7,8-trimethyl". The locants are given according to the rule of first point of difference as explained below.

Compound-6
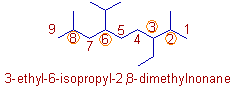
* Root word = "non"; indicating 9 carbons in the parent chain.
* Numbering of carbons according to the rule of first point of difference.
* "3-ethyl" is written before "6-isopropyl" since 'e' comes first alphabetically.
* "isopropyl" is written before "2,8-dimethyl" since 'i' precedes 'm' alphabetically. Do not compare 'i' with 'd'.
* It can be named as: 3-ethyl-2,8-dimethyl-6-(1-methylethyl)nonane or 3-ethyl-2,8-dimethyl-6-(propan-2-yl)nonane. See the explanation given for compound 4.
Compound-7
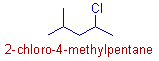
* Root word is "pent".
* Both the 'methyl' and 'chloro' groups are at equivalent positions. Hence the numbering is done such that the 'chloro' group gets lower number since it precedes the 'methyl' group alphabetically.
* Hence the IUPAC name of this organic compound is 2-chloro-4-methylpentane.
Compound-8
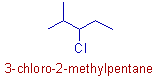
* In this molecule, the 'methyl' and 'chloro' groups are not at equivalent positions. Hence 'methyl' group is given the lower number according to the rule of first point of difference.
* However, the chloro group is written first in the name.
* Hence the IUPAC name is 3-chloro-2-methylpentane.
Compound-9
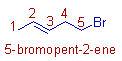
* There are 5 carbons in the parent chain. Hence the root word is 'pent'.
* There is a double bond between 2nd and 3rd carbon. Hence the primary suffix is 2-ene. The position of double bond is indicated by the lower number.
The numbering is done so as to give least number to the double bond. Since it has more priority than the 'bromo' group.
* The 'bromo' group is at 5th carbon. Hence the prefix is '5-bromo'.
* The complete name is: 5-bromo + pent + 2-ene = 5-bromopent-2-ene. It can also be written as 5-bromo-2-pentene.
Note: The complete name is (2E)-5-bromopent-2-ene. The meaning of stereo descriptor, (2E) will be explained under geometrical isomerism.
Compound-10
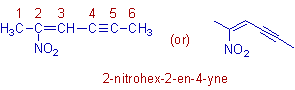
* The root word is 'hex'.
* The double bond and triple bond are indicated by the 1o prefixes: '2-ene' and '4-yne' .
* Both the double and triple bonds are at equivalent positions. Since 'ene' precedes 'yne' alphabetically, the 'ene' is given the lower number. It is also written before 'yne'
* There is a nitro group on the second carbon and is indicated by the prefix: '2-nitro'.
Note: The nitro group is not considered as a functional group in IUPAC nomenclature.
* The complete name is: 2-nitro + hex + 2-ene + 4-yne = 2-nitrohex-2-en-4-yne.
Note1: The end 'e' of ene is removed in the final name.
Note2: The complete name with the stereo descriptor is (2Z)-2-nitrohex-2-en-4-yne. See later the meaning of (2Z) under geometrical isomerism.
Compound-11
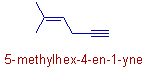
* The 'yne' is given least number since the double and triple bonds are not at equivalent positions.
It is rather confusing. This example illustrates that the IUPAC treats both double bond and triple bond at same level preference.
Compound-12
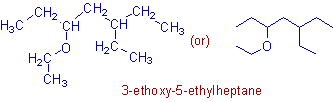
* There is an ethoxy, -OCH2CH3 group on the chain.
* Both 'ethyl' and 'ethoxy' groups are at equivalent positions.
* However among them, the ethoxy group has to be given the least number since 'o' precedes 'y' (4th letters) alphabetically.
Note: The 'alkyl' and 'ether' groups take same position in the priority order.
Compounds-13 (I) & (II)

* In above organic molecules, there are three chains with equal lengths (5 carbons) and with same number of substituents (3 in each case). However the parent chain is chosen such that it contains groups which come first in the alphabetical order.
For example, in the first compound, 2-bromo-4-chloro-3-(1-nitroethyl)pentane, the parent chain contains 'bromo' and 'chloro' since they precede 'nitro' in alphabetical order. The ethyl group contains a nitro group on its first carbon. Hence it is indicated as: '1-nitroethyl'. It is present on the 3rd carbon of the parent chain.
In the second compound, 2,4-dibromo-3-(1-chloroethyl)pentane, the parent chain is so chosen that it contains two 'bromo' groups since 'chloro' comes next alphabetically. In this case, the ethyl group contains 'chloro' group on 1st carbon of ethyl side chain. Hence it is indicated as '1-chloroethyl'.
Compound-14
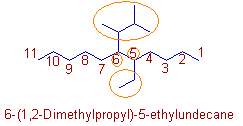
* The 1,2-Dimethylpropyl group is alphabetized under 'd' and not 'p' since the name of a complex radical is considered to begin with the first letter of its complete name. Hence it is written first in the name before the ethyl group.
Note: The 'Di' in Dimethyl propyl group does not indicate the presence of two methylpropyl radicals.
* The root word is 'undec' since there are 11 carbons in the parent chain.
* Hence the name can be written as: 6-(1,2-Dimethylpropyl)-5-ethylundecane.
* However an alternate name: 5-ethyl-6-(3-methylbutan-2-yl)undecane can also be given. See the explanation given for compound 4.
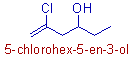
* Root word = 'hex'.
* Primary suffix = '5-ene'. Since there is a double bond between 5th and 6th carbons.
* Since there is an alcoholic functional group on 3rd carbon, the secondary suffix is given as '3-ol'. The chain is numbered such that the alcoholic group gets lower number.
Remember that a functional group must be given the priority over a double or triple bond. Hence it must be given the lower number.
* There is also a chloro group at 5th carbon. It is indicated by the prefix: 5-chloro.
* The complete name is: 5-chloro + hex + 5-ene + 3-ol = 5-chlorohex-5-en-3-ol.
The 'e' at the end of '5-ene' is removed while adding it to '3-ol'.
Compound-16
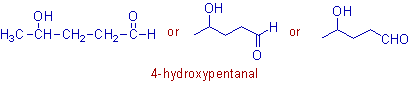
* The longest chain contains 5 carbons. The carbon of -CHO group must be included while counting the number of carbons. Hence the root word is "pent".
* There is no unsaturation between any two carbon atoms in the chain. Hence the 1o suffix is "ane".
The double bond between C=O is not considered as unsaturation for this purpose.
* There are two functional groups i.e., -OH and -CHO on the parent chain. However the -CHO group is considered as main functional group and hence the 2o suffix is "al".
* The -OH group is now considered as a substituent and hence it is to be indicated by the prefix "hydroxy".
* Since the primary functional group must be given the lower number, the numbering of carbons starts from -CHO. Hence the "hydroxy" group gets 4th locant. i.e., 4-hydroxy is the complete prefix.
* The complete name is: 4-hydroxy + pent + ane + al = 4-hydroxypentanal.
Note: There is no need to mention the locant for the -CHO group since it is at the first carbon of the chain as the main functional group.
Compound-17
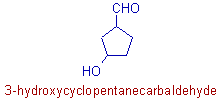
* It is a cyclic compound. There are five carbons in the ring and hence the root word is 'pent'.
Note: The carbon of -CHO group is not included.
* Since there is no unsaturation, the 1osuffix is 'ane'.
* The carbon in the primary functional group, -CHO is not the part of parent chain. Hence it is indicated by the 2o suffix: carbaldehyde.
* The infix, 'cyclo' is used to indicate the cyclic nature of the parent chain. It is immediately written before the root word 'pent'.
* There is a hydroxy group on 3rd carbon.
* The complete name is: 3-hydroxy + cyclo + pent + ane + carbaldehyde = 3-hydroxycyclopentanecarbaldehyde.
Compound-18
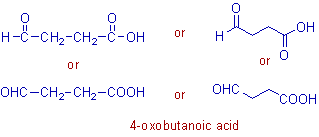
* Root word = 'but'. The carbons in -CHO and -COOH groups are included.
* The main functional group is carboxylic acid, -COOH and hence the secondary suffix is -oic acid.
* The cabonyl group, C=O of -CHO is indicated by the prefix: 4-oxo.
* The IUPAC name of this compound is: 4-oxo + but + ane + oic acid = 4-oxobutanoic acid.
Note: Again there is no need of writing the locant for 'oic acid' since it is always present at the first carbon when considered as the only main functional group.
Compound-19
![]()
* The parent chain contains 5 carbons including the carbons of -COOH groups.
* The 2o suffix is dioic acid since there are two carboxylic acid groups.
* Hence the name is pent + ane + dioic acid = pentanedioic acid.
Note: The end 'e' of ane is not removed while added to dioic acid.
Compound-20
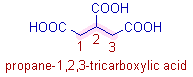
* The parent chain is selected so that it is connected to maximum number of -COOH groups. In this case it is possible to select the parent chain such that all the -COOH groups are connected to it.
The root word is 'prop' since there are three carbons in the parent chain. The carbons of -COOH groups are excluded while counting this number.
* Since the carbons of three -COOH groups do not make part of the parent chain, they are represented by the suffix 1,2,3-tricarboxylic acid.
Note: When the -COOH group is not the part of the main chain, it is indicated by the 2o suffix, carboxylic acid.
Compound-21
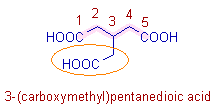
* Now it is not possible to include all the -COOH groups connected to the main chain. Therefore the parent chain is selected such that it includes the carbons of two -COOH groups (on 1st and 5th carbons). Thus the root word is 'pent'.
* Since the carbons of these two -COOH groups are now part of the parent chain, the 2o suffix must be 1,5-dioic acid.
* The group on the 3rd carbon is named as: 'carboxymethyl'. The -COOH group on this group is considered as the substituent and is indicated by the prefix, 'carboxy'.
* The complete name is: 3-(carboxymethyl) + pent + ane + dioic acid = 3-(carboxymethyl)pentanedioic acid.
Compound-22
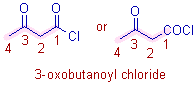
* Root word is 'but'. The carbon of COCl is also included in the parent chain.
* The main functional group is acid chloride, -COCl since it has more priority over carbonyl group, C=O.
* The 2o suffix is 'oyl chloride'.
* The C=O group at 3rd carbon is now considered as substituent and is indicated by the prefix, 3-oxo.
* The complete name is: 3-oxo + but + ane + oyl chloride = 3-oxobutanoyl chloride.
Compound-23
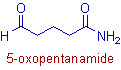
* The root word is 'pent' since there are 5 carbons in the parent chain including the carbons of aldehyde, -CHO and amide, -CONH2 groups.
* Since the main functional group is amide, the 2o suffix is 'amide'. No need of indicating the locant of amide group since it is present always at the first carbon when treated as main functional group.
* The C=O of aldehyde group is indicated by the prefix, '5-oxo'.
* The complete name if: 5-oxo + pent + ane + amide = 5-oxopentanamide.
Compound-24
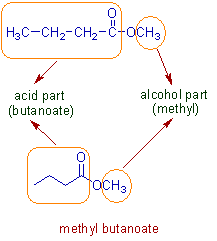
* The above molecule is an ester (represented in bond line notation also).
* The name of ester has two parts:
- The alcoholic part represented by 'alkyl'.
- The carboxylic acid part represented by 'alkanoate'.
* Thus the name of an ester can be represented as 'alkyl alkanoate'.
* In above example, the alcohol part is 'methyl' whereas the acid part is 'butanoate'.
Note: The acid part contains 4 carbons. It is considered to be derived from butanoic acid.
* The complete name is: methyl butanoate.
Compound-25
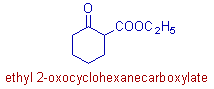
* The main functional group is ester. The acid part of the ester is derived from the cyclohexanecarboxylic acid. Hence it is indicated by cyclohexanecarboxylate. Note that the functional group is not the part of parent chain.
The alcoholic part is indicated by 'ethyl'.
* The C=O group is now considered as substituent and hence is indicated by the prefix: 2-oxo.
* Hence the complete name is ethyl 2-oxocyclohexanecarboxylate.